Country Facts:
- Capital city – Beirut
- Population – 5.6 million
- Life expectancy – 78.3 years
- Unemployment rate – 29.6%
- Below poverty line – 80%
Find more country facts on: CIA The World Factbook –Lebanon
Habitat Facts
•Habitat started in Lebanon in 2001.
•Individuals served in FY2022 ‒ 3,405
- Through market development ‒ 2,375
- Through repairs ‒ 1,030
The housing need in Lebanon
Lebanon’s modern history is characterized by a climate of political and economic instability. Positioned as a haven for the displaced, it began welcoming Palestinian refugees in 1948. Today, it shelters a staggering 1.7 million refugees, including 1.5 million Syrians, making it the country with the highest refugee concentration per capita. Internal challenges such as civil wars, rapid urbanization, and external confrontations like the 2006 Lebanon war with Israel have deeply impacted its infrastructure.
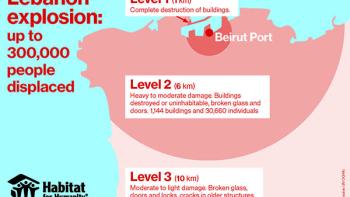
In 2019, Lebanon experienced an economic downturn that resulted in 80% of its inhabitants living in poverty. Further complications arose in 2020 when an explosion from 2,700 tons of ammonium nitrate ravaged Beirut, damaging over 200,000 homes and highlighting widespread substandard housing and limited access to essential services. To date, Habitat for Humanity Lebanon has partnered with more than 104,000 individuals through incremental and rehab construction and repairs as well as other interventions. Habitat has also engaged with over 110 volunteers through the years.
How Habitat addresses the need
Housing microfinance program
Since 2001, Habitat responded to the widespread but unmet shelter and housing needs of low-income families through a number of projects. Habitat Lebanon ran a housing microfinance program offering microloans to people who would otherwise not have access to credit. Habitat’s programming was designed to prioritize female-headed households or households with members suffering from disabilities, with subsidized loans and repayment schedules adjusted to their financial circumstances.
Responding to the Syrian refugee crisis
In 2017, Habitat began rehabilitating houses in marginalized neighborhoods with vulnerable Lebanese and non-Lebanese families. Introducing repairs to elevate home standards and enhance service access, they prioritized female-led households and those with older or disabled members. Habitat’s actions aimed to enhance WASH facility access and increase home safety and security.
School repairs
This program was designed to help public schools absorb more school-aged refugees into the formal system through renovated schools that ran second shifts to accommodate children from refugee families.
Response to Beirut port blast
In partnership with official bodies and Catholic Relief Services, Habitat addressed damage in two neighborhoods affected by the blast. They repaired cracks, leaks, doors, windows, and damaged WASH facilities, assisting 206 families and 25 businesses during pandemic lockdowns. For community cohesion, Habitat organized workshops to identify communal projects enhancing neighborhood security. Using the International Federation of the Red Cross’ Participatory Approach for Safe Shelter Awareness, communities launched projects introducing street lighting, rectifying hazardous cables, and refurbishing facades.
What you can do
DONATE
Please visit habitat.org/donate and select “Designate your donation” to donate to Habitat Lebanon.
VOLUNTEER
The Global Village program is resuming region by region until a safe and quality experience can be provided at scale worldwide. Please visit habitat.org/gov for more information.
TITHE
Habitat affiliates in the U.S. support the international work through an annual tithe. For additional information, email [email protected] or contact your local Habitat organization.
CONTACT
Email: [email protected]